For example, If your startup costs are $50,000 and your product sells for $50 with a $20 production cost, break-even analysis shows you’ll need to sell roughly 1,700 units to cover your expenses. From there, you can decide on pricing, production, and sales targets so your business can stay on the right track from the get-go. Typically, this analysis works best for businesses that focus on a single product or service.
Assumes constant selling prices
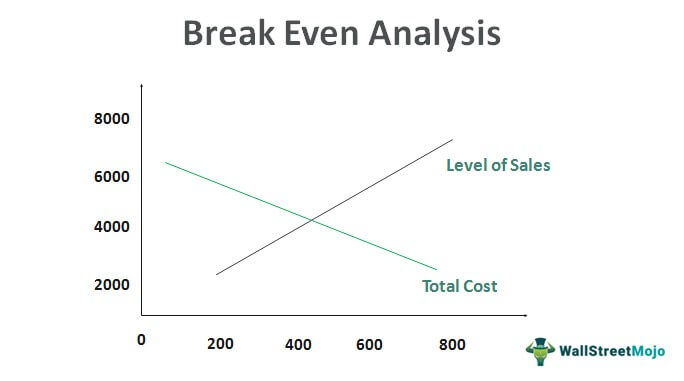
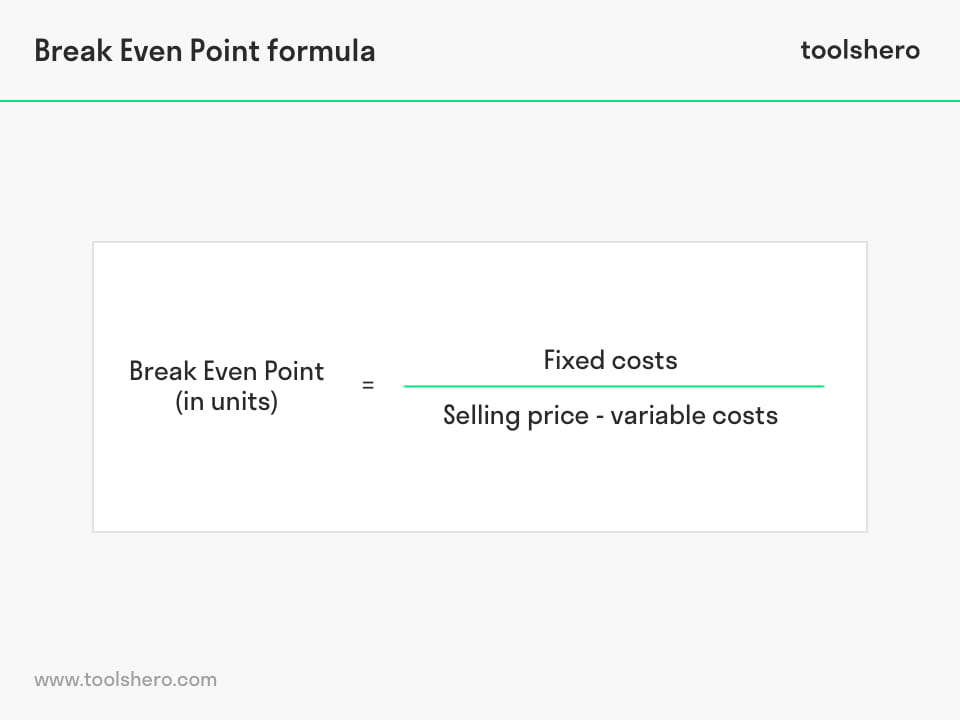
In contrast to fixed costs, variable costs increase (or decrease) based on the number of units sold. If customer demand and sales are higher for the company in a certain period, its variable costs will also move in the same direction and increase (and vice versa). The formula for calculating the break-even point (BEP) involves taking the total fixed costs and dividing the amount by the contribution margin per unit. The relationship between contribution margin and breakeven point is that even a dollar of contribution margin chips away at a company’s fixed cost.
Fixed and variable costs
- Often times you will find the need to adjust your costs and factor in things you overlooked before.
- All such information is provided solely for convenience purposes only and all users thereof should be guided accordingly.
- But what if she knows she can create only six a month given her current time and resources?
- A more advanced break-even analysis calculator would subtract out non-cash expenses from the fixed costs to compute the break-even point cash flow level.
- If they cut the price by too much and the sales forecasts for an increase in demand are inaccurate, they may cover their variable costs but not cover their fixed costs.
Upon doing so, the number of units sold cell changes to 5,000, and our net profit is equal to zero. After entering the end result being solved for (i.e., the net profit of zero), the tool determines the value of the variable (i.e., the number of units that must be sold) that makes the equation true. An unprofitable business eventually runs out of cash on hand, and its operations can no longer be sustained (e.g., compensating employees, purchasing inventory, paying office rent on time).
Explore Square and our products
A variable cost would include inventory or raw materials involved in production. Break-even analysis helps companies determine how many units need to be sold before they can cover their variable costs but also the portion of their fixed costs that are involved in producing that unit. It determines what level of sales is required to cover the total cost of business (Fixed as well as variable cost). It shows us how to calculate the point or juncture when a company would start to make a profit.
Units to sell to reach profitability
Depending on your needs, you may need to calculate your profit margin or markup to find your revenue… This will allow you to calculate the maximum price you may pay for goods, given all of your other numbers. You can also check out our markup calculator and margin calculator. In accounting, the margin of safety is the difference between actual sales and break-even sales. Managers utilize the margin of safety to know how much sales can decrease before the company or project becomes unprofitable. To calculate the break-even interest rate, you need to know the yields to maturity and the number of years left before the bonds mature.
Calculating the break-even point in sales dollars
If you’re looking for other small business tips and accounting tools, we’re here to help. QuickBooks can assist with tasks from bookkeeping and payroll to inventory analysis and profitability. Contact us today to discover what QuickBooks can do to help you with all of your small business accounting needs.
At Finance Strategists, we partner with financial experts to ensure the accuracy of our financial content. Finance Strategists has an advertising relationship with some of the companies included on this website. We may earn a commission when you click on a link or make a purchase through the links on our site. All of our content is based on objective analysis, and the opinions are our own. Using the algebraic method, we can also identify the break-even point in unit or dollar terms, as illustrated below.
The break-even price covers the cost or initial investment into something. For example, if you sell your house for exactly what you still need to pay, you would leave with zero debt but no profit. Investors who are holding a losing stock position can use an options repair strategy to break even on their investment quickly. Break-even price calculations can look different depending on the specific industry or scenario. Break-even price as a business strategy is most common in new commercial ventures, especially if a product or service is not highly differentiated from those of competitors.
For options trading, the breakeven point is the market price that an underlying asset must reach for an option buyer to avoid a loss if they exercise the option. The breakeven point doesn’t typically factor in commission costs, although these fees could be included if desired. Break-even analysis assumes that the fixed and variable costs remain constant over time. However, costs may change due to factors such as inflation, changes in technology, and changes in market conditions. It also assumes that there is a linear relationship between costs and production. Break-even analysis ignores external factors such as competition, market demand, and changes in consumer preferences.
Finally, the breakeven analysis often ignores qualitative factors such as market competition, customer satisfaction, and product quality. While the breakeven point focuses on financial metrics, successful business decisions also require a holistic view that looks outside the number. For example, it may just not be feasible to sell 10,000 units given the current market for the example above. Break-even analysis looks at fixed costs relative to the profit earned by each additional unit produced and sold. At this price, the homeowner would not see any profit, but also would not lose any money.
Check out our piece on the best bookkeeping software for small-business owners. While gathering the information you need to calculate your break-even point is tricky and time consuming, you don’t have to crunch the numbers with just a pen and paper. Any number of free online break-even point calculators can help, like this calculator by the National Association import transactions into xero for the Self-Employed. Like a lot of supposedly simple accounting principles, the break-even point is a little harder to understand than it initially appears. Let’s dive into how to calculate your break-even point and how it can guide your business. Shaun Conrad is a Certified Public Accountant and CPA exam expert with a passion for teaching.